Supply-side economics or Reaganomics:
- support policies that promote GDP growth by arguing that high marginal tax rates along w/ current system of transfer payments (i.e. unemployment compensation and social security) provide disincentives to work, invest, innovate, and take entrepreneurial adventures
- believe AS curve will determine levels of inflation, unemployment, and economics growth
Higher the tax rate you set, less $ you will collect
Laffer Curve is controversial and debatable
Laffer Curve is controversial and debatable
Criticisms:
- where economy is located on curve, it is difficult to determine
- tax cuts also ↑ demand which can fuel inflation
- empirical evidence suggests that impact on tax rates on incentives to work, save, and invest are small


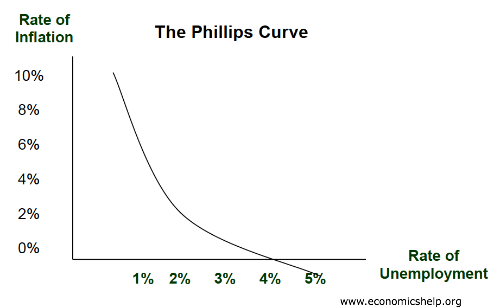
*The Phillips Curve represents the relationship b/t unemployment and inflation
*trade-off b/t unemployment and inflation occurs over SR
*each point on the Phillips Curve corresponds to a different level of output
*LRPC=long run Phillips Curve
*↑ in unemployment, LRPC →
*↓ in unemployment, LRPC ←
*Increase in AD=up/left movement along SRPC
*trade-off b/t unemployment and inflation occurs over SR
*each point on the Phillips Curve corresponds to a different level of output
*LRPC=long run Phillips Curve
- occurs at NRU
- represented by ↨ line
- no trade-off b/t unemployment and inflation in LR
- economy produces @ FE output level
- nominal wages of workers fully incorporates any changes in PL as wages adjust to inflation over the LR
*↑ in unemployment, LRPC →
*↓ in unemployment, LRPC ←
*Increase in AD=up/left movement along SRPC
- C↑, Ig↑, G↑, and/or Xn↑
- AD→: GDPR↑ and PL ↑; u%↓ and π%↑; up/left along SRPC
- this would be depicted in the graph below
- C↓, Ig↓, G↓, and/or Xn↓
- AD←: GDPR↓ and PL↓; u%↑ and π%↓; down/right along SRPC
- in this case, point B would move to point A in the graph below

Stagflation- persistent high inflation combined with high unemployment and stagnant demand in a country's economy.
Deflation- reduction of the general level of prices in an economy.
Disinflation- reduction in the rate of inflation.
